What are orthoses?
Orthosis is an in vitro device used to alter the functional properties or structure of the neuromuscular and skeletal systems. In modern times, great progress has been made in the internal and surgical treatment of neurological, muscular and skeletal diseases, but many cerebrovascular accidents, poliomyelitis, muscle weakness, bone and joint diseases still require the installation of orthopedic devices to prevent, correct malformation or compensate for lost functions.
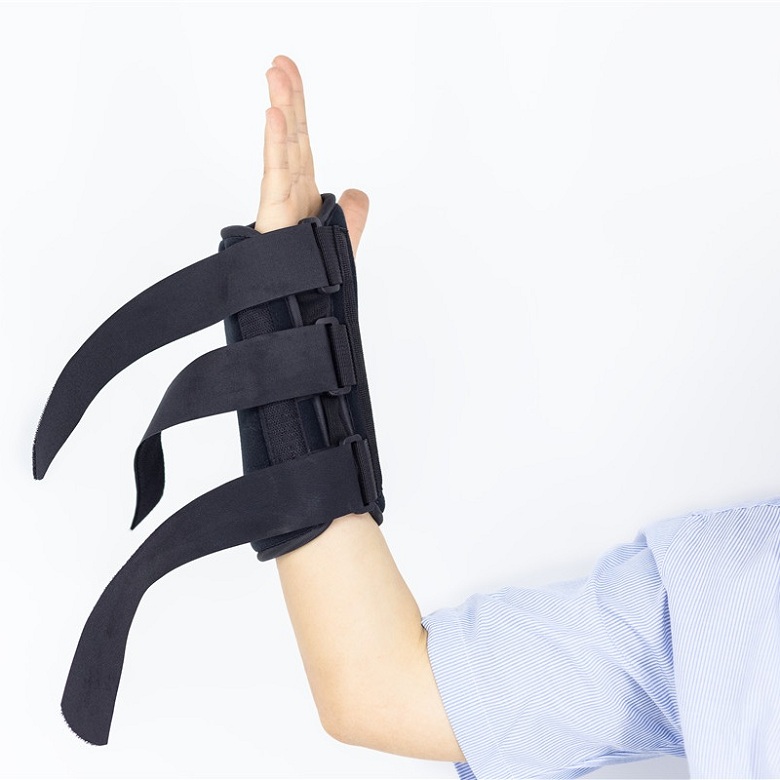

Types of orthosis
1. According to the installation location, there are three categories: Upper limb orthotic Systems, Lower limb orthotic Systems, and Spinal Orthotic Systems.
2. According to the functions and purposes of the orthotics, they are divided into orthotics for installation, protection, stability, load relief, functional, standing, walking, night, traction, and functional fracture treatment.
3, according to the main materials are divided into plastic orthosis, metal orthosis, leather orthosis, cloth orthosis.
4, according to other principles molded orthosis, externally powered orthosis, modular orthosis.
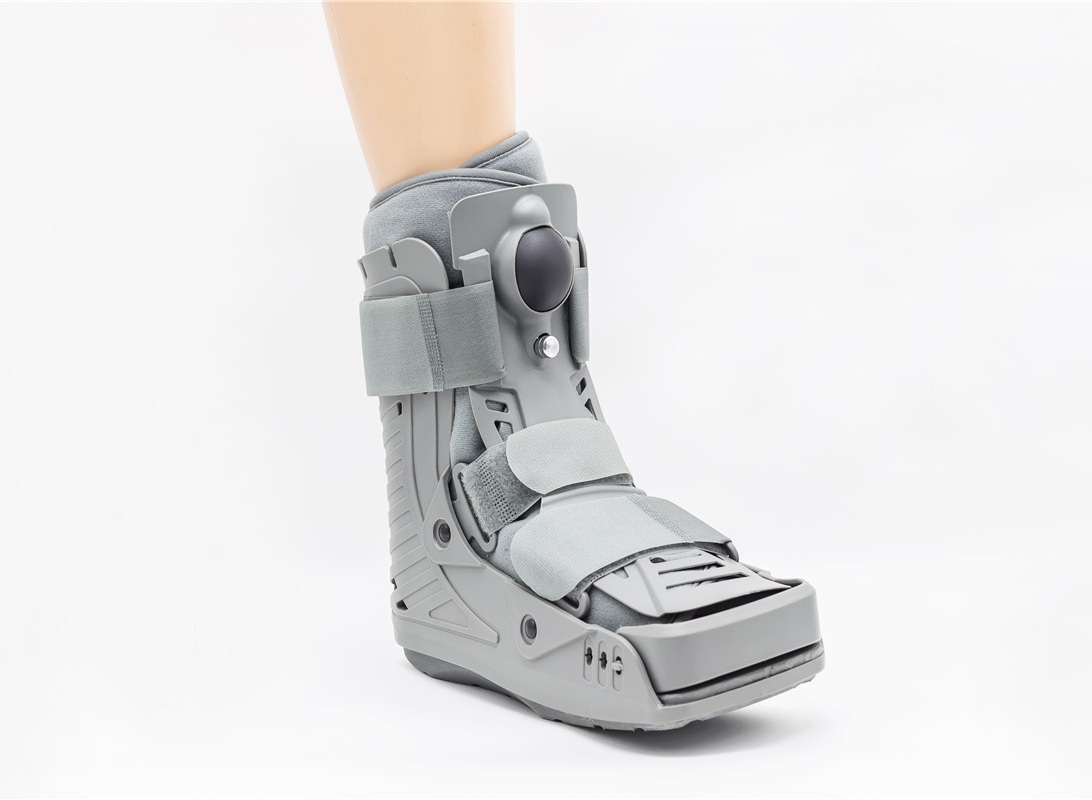

Orthoses are usually named by the abbreviation of the English name of the place where they are installed. Of course, different countries and regions have different language habits and individual search habits, so the names of orthopaedic devices are also varied. The formal naming is as follows:
Upper extremity orthoses:
Shoulder Elbow Wrist Hand Orthosis (SEWHO)
Elbow Wrist Hand Orthosis (EWHO)
Wrist Hand Orthosis (WHO)
Hand Orthosis (HO)
Lower extremity orthotics:
Hip Knee Ankle Foot Orthosis (HKAFO)
Knee Orthosis(KO)
Knee Ankle Foot Orthosis (KAFO)
Ankle Foot Orthosis (AFO)
Foot Orthosis (FO)
Spine orthotics:
Cervical Orthosis (CO)
Thorax Lumbus Sacrum Orthosis (TLSO)
Lumbus Sacrum Orthosis (LSO)
Basic functions of orthotics:
1. Stability and support
2. Prevent, correct or stabilize deformity
3. Fixation and protection
4. Remove and reduce axial load bearing of limbs
5. Inhibit muscle reflex spasm during standing and walking
6. Compensation for unequal length of limbs
7. Improve functions